In today’s digital age, self-worth is increasingly being measured in likes, shares, and followers. Social media has become a double-edged sword—a platform for self-expression and community, but also a battleground for validation and comparison. The constant need for approval from others can lead to a cycle of dependency, where self-esteem is tied to digital interactions rather than intrinsic value. This validation loop can have damaging effects on mental health and personal growth.
The Rise of the Validation Loop
Social media platforms are designed to encourage engagement. Notifications, reactions, and comments provide immediate feedback, creating a sense of gratification. Each like or positive comment triggers a release of dopamine, the brain’s “feel-good” chemical, reinforcing the behavior. Over time, users begin to associate their self-worth with the amount of positive feedback they receive online.
This validation loop is particularly prominent among younger users, who are still forming their identities and are more susceptible to external opinions. The desire to be accepted and liked becomes a driving force, influencing the way people present themselves online. Filters, curated posts, and staged photos become tools to gain approval, often at the expense of authenticity.
The Toll on Mental Health
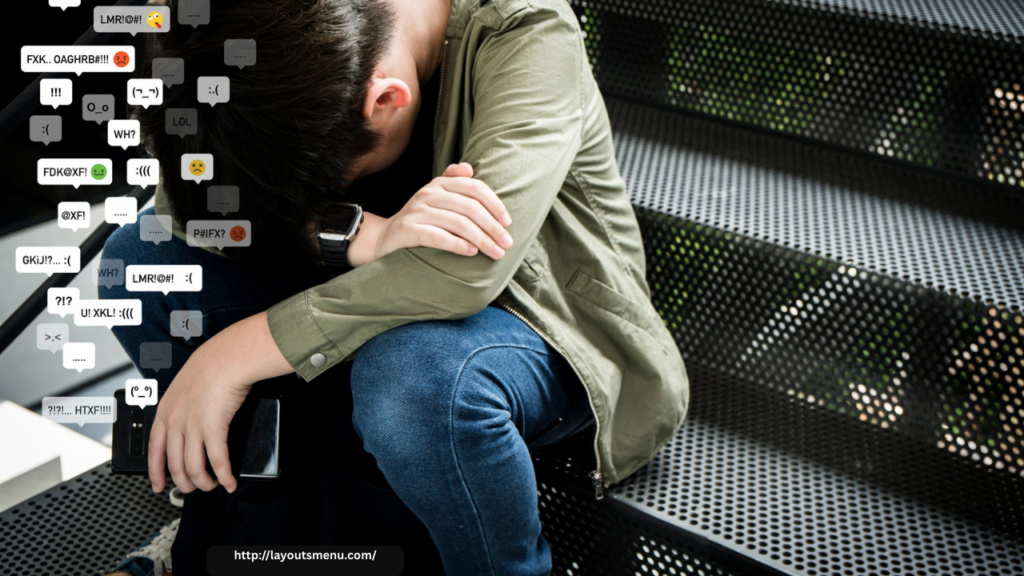
Constantly seeking validation on social media can lead to anxiety, depression, and a distorted self-image. When self-worth is measured by fluctuating metrics like likes and comments, individuals become vulnerable to feelings of inadequacy and rejection. A post that doesn’t receive the expected level of engagement can result in self-doubt and decreased self-esteem.
Moreover, the tendency to compare oneself to others on social media exacerbates the problem. Users are bombarded with highlight reels—carefully curated snapshots of others’ lives that rarely reflect reality. This can create a false sense of failure and foster negative self-perceptions, even when individuals are successful in their own right.
Breaking Free from the Cycle
Escaping the validation loop requires a conscious shift in perspective and behavior. Here are some steps to help break the cycle and foster a healthier relationship with social media:
- Limit Social Media Usage – Reducing time spent online can minimize the emotional impact of engagement metrics.
- Turn Off Notifications – Disabling alerts can help reduce the compulsion to check for validation.
- Post with Purpose – Share content that reflects your true self, not just what you think others want to see.
- Practice Self-Compassion – Remind yourself that your value is not determined by social media engagement.
- Seek Real-World Connections – Nurture relationships offline where validation comes from genuine interaction and mutual support.
Redefining Self-Worth
True self-worth comes from within. It is built on self-respect, personal values, and meaningful achievements—not the number of followers or likes on a post. By becoming aware of the validation loop and taking steps to disengage from it, individuals can reclaim their confidence and authenticity. Social media can still be a positive space when used mindfully, but it should never be the yardstick by which we measure our worth.