In an era dominated by smartphones and social media, many people find themselves trapped in the habit of “doomscrolling” — endlessly consuming negative news and content online. Although this behavior often leaves users feeling anxious, stressed, and hopeless, it is surprisingly difficult to stop. The science behind this phenomenon lies in the powerful interaction between our brain’s dopamine system and the design of social media platforms.
What is Doomscrolling?
Doomscrolling refers to the compulsive tendency to scroll through endless streams of negative news, often late into the night. Whether it’s updates about political unrest, climate change disasters, or economic downturns, our brains are wired to pay attention to threats. Evolutionarily, staying informed about dangers increased our chances of survival. However, the modern digital environment exploits this instinct, flooding us with a constant barrage of alarming information.
The Role of Dopamine
At the core of social media obsession is dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in our brain’s reward and pleasure systems. Dopamine drives motivation by making us feel good when we achieve something or anticipate a reward. Every time you find a new piece of information, get a like, or read an engaging post, your brain gets a small hit of dopamine.
This dopamine release keeps users hooked. The unpredictability of social media — not knowing whether the next post will be exciting, upsetting, or validating — creates a “variable reward schedule,” similar to what happens in gambling. It’s this unpredictability that makes social media, and doomscrolling in particular, so addictive.
Why Negative Content Captures Us
Negative content often elicits stronger emotional reactions than positive content. Fear, anger, and sadness trigger heightened brain activity, making negative news more attention-grabbing. When combined with the dopamine-driven rewards of finding new content, it becomes incredibly difficult to look away. Social media algorithms, designed to maximize engagement, tend to prioritize sensational and emotionally charged posts, further feeding the cycle.
Moreover, the act of doomscrolling gives a false sense of control. Staying updated feels like a proactive way to manage anxiety, even though the flood of bad news typically worsens it. This creates a vicious cycle where anxiety leads to more scrolling, which leads to more anxiety.
The Consequences of Doomscrolling
The mental health impacts of doomscrolling are significant. Prolonged exposure to negative news can increase stress levels, fuel anxiety and depression, disrupt sleep patterns, and lower overall emotional resilience. People who doomscroll often report feeling overwhelmed, hopeless, and disconnected from positive aspects of their lives.
Sleep deprivation is another major consequence. Exposure to blue light from screens at night suppresses melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep. Coupled with the emotional turmoil of negative content, this can lead to chronic sleep problems, further impacting mental and physical health.
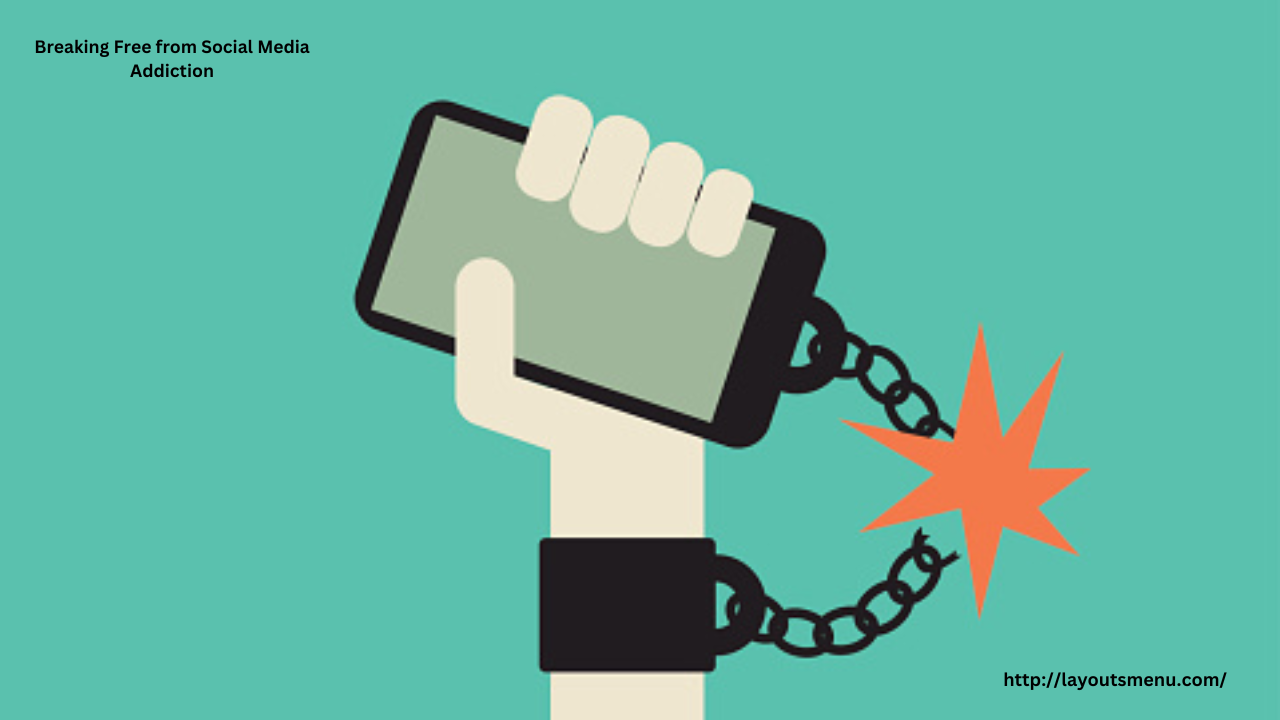
Breaking Free from the Cycle
To combat doomscrolling, it’s essential to set boundaries with social media use. Strategies include:
- Limiting screen time — Set specific times to check social media and news.
- Curating your feed — Follow accounts that post positive, uplifting content.
- Practicing mindfulness — Be aware of emotional triggers and respond intentionally rather than reactively.
- Establishing a digital curfew — Avoid screens at least an hour before bedtime to promote better sleep.
Understanding the science behind social media obsession empowers us to take control of our habits. By making conscious choices, we can break free from doomscrolling and foster healthier, more balanced digital lives.